
Hair Loss
What causes hair loss or alopecia?
Hair loss or alopecia can affect just your scalp or your entire body, and it can be temporary or permanent. It can be the result of heredity, hairstyling practices, hormonal changes, medical conditions or a normal part of aging.
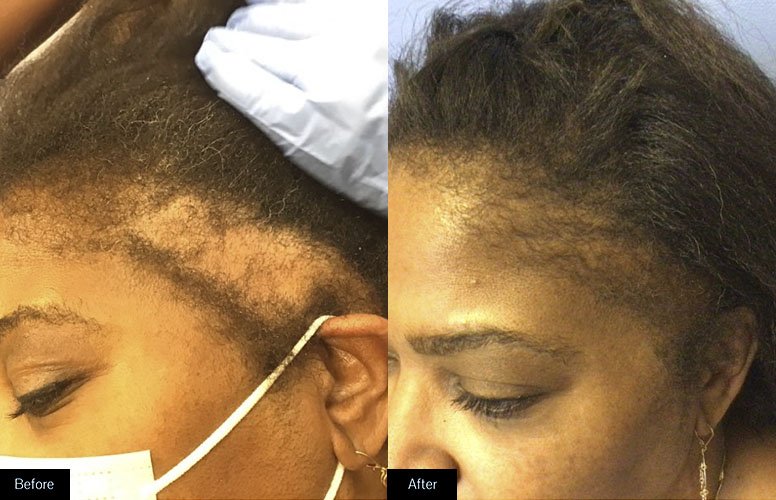
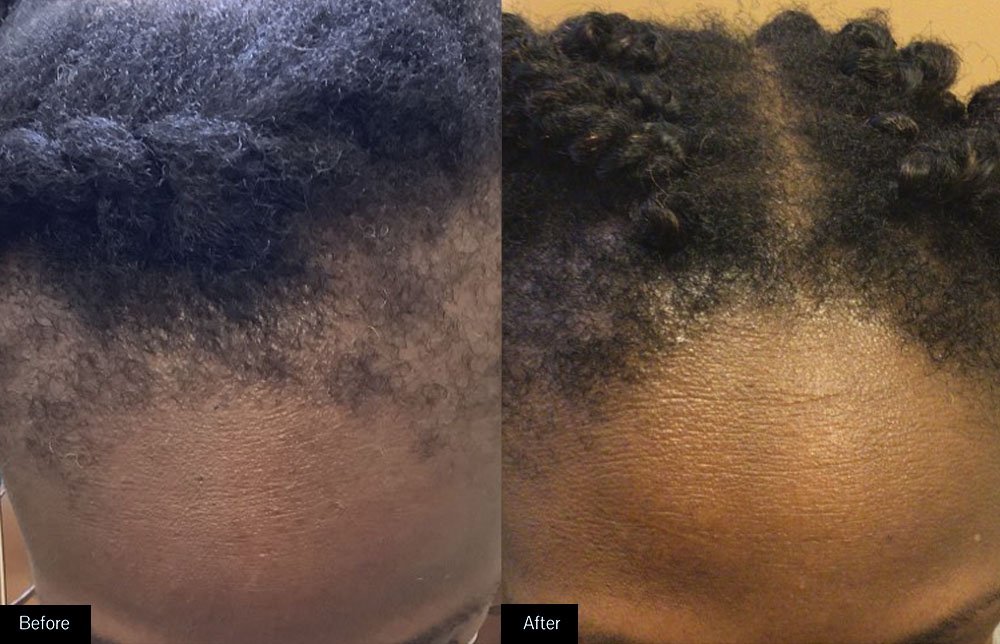
Images from Ingleton Dermatology P.C.
Treatment Options
-
Hair loss can be treated by injecting a low-dose steroid into the areas of hair loss on the scalp. This therapy is typically repeated every 6 weeks for a total of 6 treatments.
-
PRP (platelet-rich plasma) therapy for hair loss is a three-step medical treatment in which a person’s blood is drawn, processed, and then injected into the scalp.
The thought is that PRP injections trigger natural hair growth and maintain it by increasing blood supply to the hair follicle and increasing the thickness of the hair shaft. Sometimes this approach is combined with other hair loss procedures or medications.
-
Products with minoxidil help many people regrow their hair or slow the rate of hair loss or both. It'll take at least three months of treatment to prevent further hair loss and to start hair regrowth. It may take longer to tell whether the treatment is working for you. If it is helping, you'll need to continue using the medicine indefinitely to retain the benefits.
-
This is a prescription drug for men or post-menopausal women. You take it daily as a pill. Many users taking finasteride experience a slowing of hair loss, and some may show new hair growth. It may take a few months to tell whether it's working for you. You'll need to keep taking it to retain any benefits.
